clacks-overhead
How to verify Clacks Overhead
There are several ways to verify that Clacks Overhead headers have been set, either using a web browser or command line tools.
Using a web browser
In the browser, there two methods to verify the presence of the X-Clacks-Overhead header:
- Using a browser plugin
- Using the browser's Developer Tools
Using a browser plugin
There are browser plugins available for both Firefox and Chrome that can help you verify the presence of the X-Clacks-Overhead header.
- Firefox: X-Clacks-Overhead
- Chrome: Clacks Overhead - GNU Terry
- Install the plugin
- Visit a page
- Look at the plugin icon
| Chrome | Firefox | |
|---|---|---|
| Clacks active |  |
 |
| Clacks not active |  |
 |
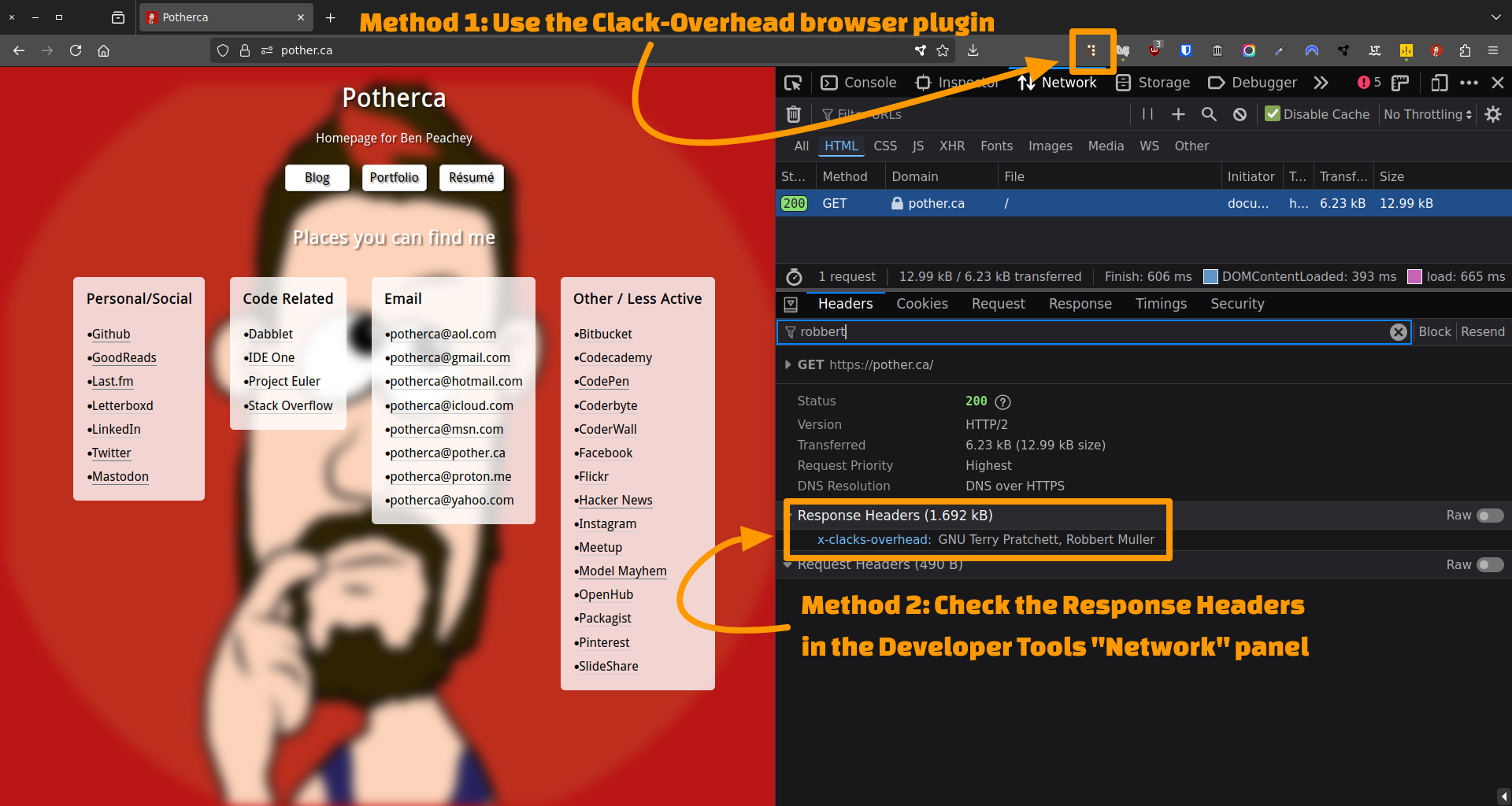
Using the browser's Developer Tools
- Visit a page
- Open the developer tools
- Visit the "Network" tab
- Reload the page
- Click on the first request in the list
- Select the "Headers" tab if it isn't already selected
- Look in the "Response Headers" section
If the page contains Clacks Overhead headers, you should see a header named X-Clacks-Overhead with the value GNU Robbert Muller.
Using a command line tool
There are various tools that can be used to check for the presence of the X-Clacks-Overhead header in the HTTP response.
After opening a terminal or command prompt, run an appropriate command based on the tool you prefer:
Replacing https://example.com in the examples below with the URL of the page to check).
If the header is present, you should see output similar to:
x-clacks-overhead: GNU Robbert Muller
If the header is not present, there will be no output.
Using curl
curl --head --silent https://example.com | grep --ignore-case clacks
Using wget
wget --quiet --server-response --spider https://example.com 2>&1 | grep --ignore-case clacks